课程训练
对称密码学
我们可以将对称密钥密码分为两种类型:分组密码和流密码。分组密码将明文分解为固定长度的块,并通过加密函数与密钥一起发送每个块。同时,流密码通过将伪随机密钥流与数据进行异或,一次加密一个字节的明文。 AES 是一种分组密码,但可以使用 CTR 等操作模式转换为流密码。
AES工作原理
Keyed Permutations(键控排列)
与所有好的分组密码一样,AES 执行“密钥排列”。这意味着它将每个可能的输入块映射到唯一的输出块,并用一个键确定要执行的排列。
“块”仅指固定数量的位或字节,它可以表示任何类型的数据。 AES 处理一个块并输出另一个块。我们将具体讨论 AES 的变体,它适用于 128 位(16 字节)块和 128 位密钥,称为 AES-128。
使用相同的密钥,可以反向执行排列,将输出块映射回原始输入块。输入和输出块之间存在一对一的对应关系非常重要,否则我们将无法依赖密文解密回与我们开始时相同的明文。
一对一对应的数学术语是什么?
crypto{bijection}Resisting Bruteforce(抵抗暴力)
crypto{Biclique Cryptanalysis}Structure of AES(AES的结构)
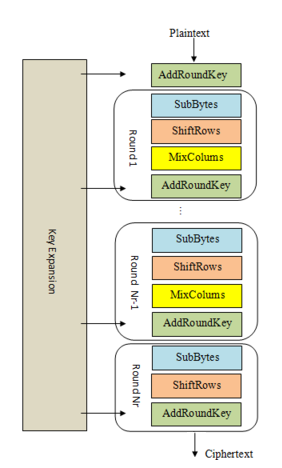
以下是 AES 加密各个阶段的概述:
1.密钥扩展或密钥计划
从 128 位密钥中,派生出 11 个独立的 128 位 “轮密钥”:每个 AddRoundKey 步骤中使用一个。
2.初始密钥添加
AddRoundKey —— 第一轮密钥的字节与状态的字节进行异或。
3.回合- 该阶段循环 10 次,即 9 个主回合加上一个“最后回合”
(a) SubBytes(字节替换) —— 根据查找表(“S 盒”)将状态的每个字节替换为不同的字节。
(b) ShiftRows(行变换)——状态矩阵的最后三行被转置——移位一列、两列或三列。
(c) MixColumns(列变换) —— 对状态的列执行矩阵乘法,组合每列中的四个字节。这在最后一轮中被跳过。
(d) AddRoundKey(轮密钥相加)- 当前轮密钥的字节与状态的字节进行异或。
YouTube :以 Flash 动画形式解释 AES Rijndael 密码
matrix = [
[99, 114, 121, 112],
[116, 111, 123, 105],
[110, 109, 97, 116],
[114, 105, 120, 125],
]
ints = []
for i in matrix:
for j in range(len(i)):
ints.append(i[j])
print(ints)
for n in ints:
print(chr(n),end="")Round Keys(轮密钥)
state = [
[206, 243, 61, 34],
[171, 11, 93, 31],
[16, 200, 91, 108],
[150, 3, 194, 51],
]
round_key = [
[173, 129, 68, 82],
[223, 100, 38, 109],
[32, 189, 53, 8],
[253, 48, 187, 78],
]
def add_round_key(s, k):
key = []
for i in range(len(s)):
# print(s[i])
for j in range(4):
m = (s[i][j]) ^ (k[i][j])
key.append(m)
return key
flag = add_round_key(state, round_key)
for i in flag:
print(chr(i),end="")Confusion through Substitution(通过替换混淆)
s_box = (
0x63, 0x7C, 0x77, 0x7B, 0xF2, 0x6B, 0x6F, 0xC5, 0x30, 0x01, 0x67, 0x2B, 0xFE, 0xD7, 0xAB, 0x76,
0xCA, 0x82, 0xC9, 0x7D, 0xFA, 0x59, 0x47, 0xF0, 0xAD, 0xD4, 0xA2, 0xAF, 0x9C, 0xA4, 0x72, 0xC0,
0xB7, 0xFD, 0x93, 0x26, 0x36, 0x3F, 0xF7, 0xCC, 0x34, 0xA5, 0xE5, 0xF1, 0x71, 0xD8, 0x31, 0x15,
0x04, 0xC7, 0x23, 0xC3, 0x18, 0x96, 0x05, 0x9A, 0x07, 0x12, 0x80, 0xE2, 0xEB, 0x27, 0xB2, 0x75,
0x09, 0x83, 0x2C, 0x1A, 0x1B, 0x6E, 0x5A, 0xA0, 0x52, 0x3B, 0xD6, 0xB3, 0x29, 0xE3, 0x2F, 0x84,
0x53, 0xD1, 0x00, 0xED, 0x20, 0xFC, 0xB1, 0x5B, 0x6A, 0xCB, 0xBE, 0x39, 0x4A, 0x4C, 0x58, 0xCF,
0xD0, 0xEF, 0xAA, 0xFB, 0x43, 0x4D, 0x33, 0x85, 0x45, 0xF9, 0x02, 0x7F, 0x50, 0x3C, 0x9F, 0xA8,
0x51, 0xA3, 0x40, 0x8F, 0x92, 0x9D, 0x38, 0xF5, 0xBC, 0xB6, 0xDA, 0x21, 0x10, 0xFF, 0xF3, 0xD2,
0xCD, 0x0C, 0x13, 0xEC, 0x5F, 0x97, 0x44, 0x17, 0xC4, 0xA7, 0x7E, 0x3D, 0x64, 0x5D, 0x19, 0x73,
0x60, 0x81, 0x4F, 0xDC, 0x22, 0x2A, 0x90, 0x88, 0x46, 0xEE, 0xB8, 0x14, 0xDE, 0x5E, 0x0B, 0xDB,
0xE0, 0x32, 0x3A, 0x0A, 0x49, 0x06, 0x24, 0x5C, 0xC2, 0xD3, 0xAC, 0x62, 0x91, 0x95, 0xE4, 0x79,
0xE7, 0xC8, 0x37, 0x6D, 0x8D, 0xD5, 0x4E, 0xA9, 0x6C, 0x56, 0xF4, 0xEA, 0x65, 0x7A, 0xAE, 0x08,
0xBA, 0x78, 0x25, 0x2E, 0x1C, 0xA6, 0xB4, 0xC6, 0xE8, 0xDD, 0x74, 0x1F, 0x4B, 0xBD, 0x8B, 0x8A,
0x70, 0x3E, 0xB5, 0x66, 0x48, 0x03, 0xF6, 0x0E, 0x61, 0x35, 0x57, 0xB9, 0x86, 0xC1, 0x1D, 0x9E,
0xE1, 0xF8, 0x98, 0x11, 0x69, 0xD9, 0x8E, 0x94, 0x9B, 0x1E, 0x87, 0xE9, 0xCE, 0x55, 0x28, 0xDF,
0x8C, 0xA1, 0x89, 0x0D, 0xBF, 0xE6, 0x42, 0x68, 0x41, 0x99, 0x2D, 0x0F, 0xB0, 0x54, 0xBB, 0x16,
)
inv_s_box = (
0x52, 0x09, 0x6A, 0xD5, 0x30, 0x36, 0xA5, 0x38, 0xBF, 0x40, 0xA3, 0x9E, 0x81, 0xF3, 0xD7, 0xFB,
0x7C, 0xE3, 0x39, 0x82, 0x9B, 0x2F, 0xFF, 0x87, 0x34, 0x8E, 0x43, 0x44, 0xC4, 0xDE, 0xE9, 0xCB,
0x54, 0x7B, 0x94, 0x32, 0xA6, 0xC2, 0x23, 0x3D, 0xEE, 0x4C, 0x95, 0x0B, 0x42, 0xFA, 0xC3, 0x4E,
0x08, 0x2E, 0xA1, 0x66, 0x28, 0xD9, 0x24, 0xB2, 0x76, 0x5B, 0xA2, 0x49, 0x6D, 0x8B, 0xD1, 0x25,
0x72, 0xF8, 0xF6, 0x64, 0x86, 0x68, 0x98, 0x16, 0xD4, 0xA4, 0x5C, 0xCC, 0x5D, 0x65, 0xB6, 0x92,
0x6C, 0x70, 0x48, 0x50, 0xFD, 0xED, 0xB9, 0xDA, 0x5E, 0x15, 0x46, 0x57, 0xA7, 0x8D, 0x9D, 0x84,
0x90, 0xD8, 0xAB, 0x00, 0x8C, 0xBC, 0xD3, 0x0A, 0xF7, 0xE4, 0x58, 0x05, 0xB8, 0xB3, 0x45, 0x06,
0xD0, 0x2C, 0x1E, 0x8F, 0xCA, 0x3F, 0x0F, 0x02, 0xC1, 0xAF, 0xBD, 0x03, 0x01, 0x13, 0x8A, 0x6B,
0x3A, 0x91, 0x11, 0x41, 0x4F, 0x67, 0xDC, 0xEA, 0x97, 0xF2, 0xCF, 0xCE, 0xF0, 0xB4, 0xE6, 0x73,
0x96, 0xAC, 0x74, 0x22, 0xE7, 0xAD, 0x35, 0x85, 0xE2, 0xF9, 0x37, 0xE8, 0x1C, 0x75, 0xDF, 0x6E,
0x47, 0xF1, 0x1A, 0x71, 0x1D, 0x29, 0xC5, 0x89, 0x6F, 0xB7, 0x62, 0x0E, 0xAA, 0x18, 0xBE, 0x1B,
0xFC, 0x56, 0x3E, 0x4B, 0xC6, 0xD2, 0x79, 0x20, 0x9A, 0xDB, 0xC0, 0xFE, 0x78, 0xCD, 0x5A, 0xF4,
0x1F, 0xDD, 0xA8, 0x33, 0x88, 0x07, 0xC7, 0x31, 0xB1, 0x12, 0x10, 0x59, 0x27, 0x80, 0xEC, 0x5F,
0x60, 0x51, 0x7F, 0xA9, 0x19, 0xB5, 0x4A, 0x0D, 0x2D, 0xE5, 0x7A, 0x9F, 0x93, 0xC9, 0x9C, 0xEF,
0xA0, 0xE0, 0x3B, 0x4D, 0xAE, 0x2A, 0xF5, 0xB0, 0xC8, 0xEB, 0xBB, 0x3C, 0x83, 0x53, 0x99, 0x61,
0x17, 0x2B, 0x04, 0x7E, 0xBA, 0x77, 0xD6, 0x26, 0xE1, 0x69, 0x14, 0x63, 0x55, 0x21, 0x0C, 0x7D,
)
state =[251, 64, 182, 81,146, 168, 33, 80,199, 159, 195, 24,64, 80, 182, 255]
def sub_bytes(s):
for i in range(len(state)):
state[i] = s_box[state[i]]
def sub_bytesInv(s):
for i in range(len(s)):
state[i] = inv_s_box[state[i]]
# sub_bytes(state)
# print(state)
sub_bytesInv(state)
print(state)
for i in state:
print(chr(i),end="")Diffusion through Permutation(通过置换扩散)
def shift_rows(s):
s[0][1], s[1][1], s[2][1], s[3][1] = s[1][1], s[2][1], s[3][1], s[0][1]
s[0][2], s[1][2], s[2][2], s[3][2] = s[2][2], s[3][2], s[0][2], s[1][2]
s[0][3], s[1][3], s[2][3], s[3][3] = s[3][3], s[0][3], s[1][3], s[2][3]
def inv_shift_rows(s):
s[0][1], s[1][1], s[2][1], s[3][1] = s[3][1], s[0][1], s[1][1], s[2][1]
s[0][2], s[1][2], s[2][2], s[3][2] = s[2][2], s[3][2], s[0][2], s[1][2]
s[0][3], s[1][3], s[2][3], s[3][3] = s[1][3], s[2][3], s[3][3], s[0][3]
# learned from http://cs.ucsb.edu/~koc/cs178/projects/JT/aes.c
xtime = lambda a: (((a << 1) ^ 0x1B) & 0xFF) if (a & 0x80) else (a << 1)
def mix_single_column(a):
# see Sec 4.1.2 in The Design of Rijndael
t = a[0] ^ a[1] ^ a[2] ^ a[3]
u = a[0]
a[0] ^= t ^ xtime(a[0] ^ a[1])
a[1] ^= t ^ xtime(a[1] ^ a[2])
a[2] ^= t ^ xtime(a[2] ^ a[3])
a[3] ^= t ^ xtime(a[3] ^ u)
def mix_columns(s):
for i in range(4):
mix_single_column(s[i])
def inv_mix_columns(s):
# see Sec 4.1.3 in The Design of Rijndael
for i in range(4):
u = xtime(xtime(s[i][0] ^ s[i][2]))
v = xtime(xtime(s[i][1] ^ s[i][3]))
s[i][0] ^= u
s[i][1] ^= v
s[i][2] ^= u
s[i][3] ^= v
mix_columns(s)
state = [
[108, 106, 71, 86],
[96, 62, 38, 72],
[42, 184, 92, 209],
[94, 79, 8, 54],
]
inv_mix_columns(state)
print(state)
inv_shift_rows(state)
print(state)
print(bytes(sum(state, [])))
result = [99, 114, 121, 112,116, 111, 123, 100,49, 102, 102, 85,115, 51, 82, 125]
for i in result:
print(chr(i),end="")Bringing It All Together(把所有整合在一起)
对称密码入门
Modes of Operation Starter
Passwords as Keys
分组密码
ECB Oracle
ECB CBC WTF
Flipping Cookie
流密码
Symmetry
Bean Counter
公钥密码学
RSA Starter 1
print(pow(101,17,22663))RSA Starter 2
m = 12
p=17
q=23
n = p*q
e=65537
print(pow(m,e,n))RSA Starter 3
p = 857504083339712752489993810777
q = 1029224947942998075080348647219
Phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
print(phi)RSA Starter 4
from gmpy2 import *
p = 857504083339712752489993810777
q = 1029224947942998075080348647219
e=65537
phi = (q-1)*(p-1)
d = invert(e,phi)
print(d)RSA Starter 5
from gmpy2 import *
N = 882564595536224140639625987659416029426239230804614613279163
e = 65537
c = 77578995801157823671636298847186723593814843845525223303932
p = 857504083339712752489993810777
q = 1029224947942998075080348647219
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
d = d = invert(e,phi)
print(pow(c,d,N))RSA Starter 6
from gmpy2 import *
from libnum import*
from hashlib import sha256
N = 15216583654836731327639981224133918855895948374072384050848479908982286890731769486609085918857664046075375253168955058743185664390273058074450390236774324903305663479046566232967297765731625328029814055635316002591227570271271445226094919864475407884459980489638001092788574811554149774028950310695112688723853763743238753349782508121985338746755237819373178699343135091783992299561827389745132880022259873387524273298850340648779897909381979714026837172003953221052431217940632552930880000919436507245150726543040714721553361063311954285289857582079880295199632757829525723874753306371990452491305564061051059885803
d = 11175901210643014262548222473449533091378848269490518850474399681690547281665059317155831692300453197335735728459259392366823302405685389586883670043744683993709123180805154631088513521456979317628012721881537154107239389466063136007337120599915456659758559300673444689263854921332185562706707573660658164991098457874495054854491474065039621922972671588299315846306069845169959451250821044417886630346229021305410340100401530146135418806544340908355106582089082980533651095594192031411679866134256418292249592135441145384466261279428795408721990564658703903787956958168449841491667690491585550160457893350536334242689
flag = b'crypto{Immut4ble_m3ssag1ng}'
h = sha256(flag).hexdigest()
# print(h)
enc = pow(int(h,16),d,N)
print(hex(enc)[2:])Factoring
#http://factordb.com/index.php?query=510143758735509025530880200653196460532653147
19704762736204164635843Monoprime
from gmpy2 import *
from libnum import *
n = 171731371218065444125482536302245915415603318380280392385291836472299752747934607246477508507827284075763910264995326010251268493630501989810855418416643352631102434317900028697993224868629935657273062472544675693365930943308086634291936846505861203914449338007760990051788980485462592823446469606824421932591
e = 65537
ct = 161367550346730604451454756189028938964941280347662098798775466019463375610700074840105776873791605070092554650190486030367121011578171525759600774739890458414593857709994072516290998135846956596662071379067305011746842247628316996977338024343628757374524136260758515864509435302781735938531030576289086798942
phi = (n-1)
d = invert(e,phi)
print(n2s(int(pow(ct,d,n))))Manyprime
可以使用 sage 的 ecm.factor() 函数对模数 n 进行因式分解。
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
n=580642391898843192929563856870897799650883152718761762932292482252152591279871421569162037190419036435041797739880389529593674485555792234900969402019055601781662044515999210032698275981631376651117318677368742867687180140048715627160641771118040372573575479330830092989800730105573700557717146251860588802509310534792310748898504394966263819959963273509119791037525504422606634640173277598774814099540555569257179715908642917355365791447508751401889724095964924513196281345665480688029639999472649549163147599540142367575413885729653166517595719991872223011969856259344396899748662101941230745601719730556631637
e=65537
ct=320721490534624434149993723527322977960556510750628354856260732098109692581338409999983376131354918370047625150454728718467998870322344980985635149656977787964380651868131740312053755501594999166365821315043312308622388016666802478485476059625888033017198083472976011719998333985531756978678758897472845358167730221506573817798467100023754709109274265835201757369829744113233607359526441007577850111228850004361838028842815813724076511058179239339760639518034583306154826603816927757236549096339501503316601078891287408682099750164720032975016814187899399273719181407940397071512493967454225665490162619270814464
P=[9282105380008121879, 9303850685953812323, 9389357739583927789, 10336650220878499841, 10638241655447339831, 11282698189561966721, 11328768673634243077, 11403460639036243901, 11473665579512371723, 11492065299277279799, 11530534813954192171, 11665347949879312361, 12132158321859677597, 12834461276877415051, 12955403765595949597, 12973972336777979701, 13099895578757581201, 13572286589428162097, 14100640260554622013, 14178869592193599187, 14278240802299816541, 14523070016044624039, 14963354250199553339, 15364597561881860737, 15669758663523555763, 15824122791679574573, 15998365463074268941, 16656402470578844539, 16898740504023346457, 17138336856793050757, 17174065872156629921, 17281246625998849649]
phi=1
for i in P:
phi *= (i-1)
d=invert(e,phi)
m=pow(ct,d,n)
flag=long_to_bytes(m)
print(flag)Salty
from Crypto.Util.number import *
ct = 44981230718212183604274785925793145442655465025264554046028251311164494127485
flag=long_to_bytes(ct)
print(flag)Modulus Inutilis
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
e = 3
ct = 243251053617903760309941844835411292373350655973075480264001352919865180151222189820473358411037759381328642957324889519192337152355302808400638052620580409813222660643570085177957
flag=long_to_bytes(iroot(ct,3)[0])
print(flag)Diffie-Hellman Starter 1
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from gmpy2 import *
p = 991
g = 209
flag=invert(g,p)
print(flag)Diffie-Hellman Starter 2
求有限域 Fp ,p = 28151 上的原根
sage: gp('znprimroot(28151)')
Out : Mod(7, 28151)法二:
GF(28151).primitive_element() #计算原根法三:
GF(28151,modulus="primitive").gen()Diffie-Hellman Starter 3
g = 2
a = 972107443837033796245864316200458246846904598488981605856765890478853088246897345487328491037710219222038930943365848626194109830309179393018216763327572120124760140018038673999837643377590434413866611132403979547150659053897355593394492586978400044375465657296027592948349589216415363722668361328689588996541370097559090335137676411595949335857341797148926151694299575970292809805314431447043469447485957669949989090202320234337890323293401862304986599884732815
p = 2410312426921032588552076022197566074856950548502459942654116941958108831682612228890093858261341614673227141477904012196503648957050582631942730706805009223062734745341073406696246014589361659774041027169249453200378729434170325843778659198143763193776859869524088940195577346119843545301547043747207749969763750084308926339295559968882457872412993810129130294592999947926365264059284647209730384947211681434464714438488520940127459844288859336526896320919633919
print(pow(g,a,p))Diffie-Hellman Starter 4
Alice 计算共享密钥
A = 70249943217595468278554541264975482909289174351516133994495821400710625291840101960595720462672604202133493023241393916394629829526272643847352371534839862030410331485087487331809285533195024369287293217083414424096866925845838641840923193480821332056735592483730921055532222505605661664236182285229504265881752580410194731633895345823963910901731715743835775619780738974844840425579683385344491015955892106904647602049559477279345982530488299847663103078045601
b = 12019233252903990344598522535774963020395770409445296724034378433497976840167805970589960962221948290951873387728102115996831454482299243226839490999713763440412177965861508773420532266484619126710566414914227560103715336696193210379850575047730388378348266180934946139100479831339835896583443691529372703954589071507717917136906770122077739814262298488662138085608736103418601750861698417340264213867753834679359191427098195887112064503104510489610448294420720
p = 2410312426921032588552076022197566074856950548502459942654116941958108831682612228890093858261341614673227141477904012196503648957050582631942730706805009223062734745341073406696246014589361659774041027169249453200378729434170325843778659198143763193776859869524088940195577346119843545301547043747207749969763750084308926339295559968882457872412993810129130294592999947926365264059284647209730384947211681434464714438488520940127459844288859336526896320919633919
print(pow(A,b,p))Diffie-Hellman Starter 5
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
import hashlib
def is_pkcs7_padded(message):
padding = message[-message[-1]:]
return all(padding[i] == len(padding) for i in range(0, len(padding)))
def decrypt_flag(shared_secret: int, iv: str, ciphertext: str):
# Derive AES key from shared secret
sha1 = hashlib.sha1()
sha1.update(str(shared_secret).encode('ascii'))
key = sha1.digest()[:16]
# Decrypt flag
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
iv = bytes.fromhex(iv)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
if is_pkcs7_padded(plaintext):
return unpad(plaintext, 16).decode('ascii')
else:
return plaintext.decode('ascii')
A = 112218739139542908880564359534373424013016249772931962692237907571990334483528877513809272625610512061159061737608547288558662879685086684299624481742865016924065000555267977830144740364467977206555914781236397216033805882207640219686011643468275165718132888489024688846101943642459655423609111976363316080620471928236879737944217503462265615774774318986375878440978819238346077908864116156831874695817477772477121232820827728424890845769152726027520772901423784
b = 197395083814907028991785772714920885908249341925650951555219049411298436217190605190824934787336279228785809783531814507661385111220639329358048196339626065676869119737979175531770768861808581110311903548567424039264485661330995221907803300824165469977099494284722831845653985392791480264712091293580274947132480402319812110462641143884577706335859190668240694680261160210609506891842793868297672619625924001403035676872189455767944077542198064499486164431451944
p = 2410312426921032588552076022197566074856950548502459942654116941958108831682612228890093858261341614673227141477904012196503648957050582631942730706805009223062734745341073406696246014589361659774041027169249453200378729434170325843778659198143763193776859869524088940195577346119843545301547043747207749969763750084308926339295559968882457872412993810129130294592999947926365264059284647209730384947211681434464714438488520940127459844288859336526896320919633919
shared_secret = pow(A,b,p)
iv = '737561146ff8194f45290f5766ed6aba'
ciphertext = '39c99bf2f0c14678d6a5416faef954b5893c316fc3c48622ba1fd6a9fe85f3dc72a29c394cf4bc8aff6a7b21cae8e12c'
print(decrypt_flag(shared_secret, iv, ciphertext))Parameter Injection
https://cryptopals.com/sets/5/challenges/34

解法一:通过交互式服务器获取数据
Intercepted from Alice: {"p": "0xffffffffffffffffc90fdaa22168c234c4c6628b80dc1cd129024e088a67cc74020bbea63b139b22514a08798e3404ddef9519b3cd3a431b302b0a6df25f14374fe1356d6d51c245e485b576625e7ec6f44c42e9a637ed6b0bff5cb6f406b7edee386bfb5a899fa5ae9f24117c4b1fe649286651ece45b3dc2007cb8a163bf0598da48361c55d39a69163fa8fd24cf5f83655d23dca3ad961c62f356208552bb9ed529077096966d670c354e4abc9804f1746c08ca237327ffffffffffffffff", "g": "0x02", "A": "0x91c83366ff1a5701ea82a0228d48e4cb20d96713ef6ecd9132bb59cf6ac4d5e16010eceefdf0669b7a722b093d80ec65dfbee8879d873100dad709be68c8bfd619844dd51dcacc3198b8e94e6770a1d69a194f79a4c6504dd2e02cbd41bd76dc00d52aaa99094fbc3cdc5112768b521bac62dd364471a5ec6c7f68996ea3a0ee0582fbb61820d78f1902eb3165b800a621d2e7e29f3aef222330a311a91dcdca0b49ca32c081a5cce376638d4404f81999040118cac275d2646041ad926629d0"}从 Alice 处获得数据 p,g,A,由 DH 算法可知 :
Bob得到后进行共享密钥生成得到:
Send to Bob: {"p": "0xffffffffffffffffc90fdaa22168c234c4c6628b80dc1cd129024e088a67cc74020bbea63b139b22514a08798e3404ddef9519b3cd3a431b302b0a6df25f14374fe1356d6d51c245e485b576625e7ec6f44c42e9a637ed6b0bff5cb6f406b7edee386bfb5a899fa5ae9f24117c4b1fe649286651ece45b3dc2007cb8a163bf0598da48361c55d39a69163fa8fd24cf5f83655d23dca3ad961c62f356208552bb9ed529077096966d670c354e4abc9804f1746c08ca237327ffffffffffffffff","g": "0x02","A": "0xffffffffffffffffc90fdaa22168c234c4c6628b80dc1cd129024e088a67cc74020bbea63b139b22514a08798e3404ddef9519b3cd3a431b302b0a6df25f14374fe1356d6d51c245e485b576625e7ec6f44c42e9a637ed6b0bff5cb6f406b7edee386bfb5a899fa5ae9f24117c4b1fe649286651ece45b3dc2007cb8a163bf0598da48361c55d39a69163fa8fd24cf5f83655d23dca3ad961c62f356208552bb9ed529077096966d670c354e4abc9804f1746c08ca237327ffffffffffffffff"}
Intercepted from Bob: {"B": "0xcbf586f3406f21f6b8e65068b7141dff0768aadc8667a1c94eec5c3ba5f7907324eba3d4316490868ddac5b00a1be5a03234957141aa22ba15fad7731777d27cfac6a008c40ed30fec93d2a80e36047864c931c3e32df6fd1f886068f7c808300cfa7bf46730fb2394829799c350ccb0f165083f59402bb8f418b4b57020cf48faa417cd96fc7195cbed79507bf5eb208ef15af1f4731e3f556eadbdb2e6b23ec163df2ee89073d77867ac2bf43222d7858fd070f40021c4db8f7a9ea48fdee8"}
Send to Alice: {"p": "0xffffffffffffffffc90fdaa22168c234c4c6628b80dc1cd129024e088a67cc74020bbea63b139b22514a08798e3404ddef9519b3cd3a431b302b0a6df25f14374fe1356d6d51c245e485b576625e7ec6f44c42e9a637ed6b0bff5cb6f406b7edee386bfb5a899fa5ae9f24117c4b1fe649286651ece45b3dc2007cb8a163bf0598da48361c55d39a69163fa8fd24cf5f83655d23dca3ad961c62f356208552bb9ed529077096966d670c354e4abc9804f1746c08ca237327ffffffffffffffff","g": "0x02","B": "0xffffffffffffffffc90fdaa22168c234c4c6628b80dc1cd129024e088a67cc74020bbea63b139b22514a08798e3404ddef9519b3cd3a431b302b0a6df25f14374fe1356d6d51c245e485b576625e7ec6f44c42e9a637ed6b0bff5cb6f406b7edee386bfb5a899fa5ae9f24117c4b1fe649286651ece45b3dc2007cb8a163bf0598da48361c55d39a69163fa8fd24cf5f83655d23dca3ad961c62f356208552bb9ed529077096966d670c354e4abc9804f1746c08ca237327ffffffffffffffff"}
Intercepted from Alice: {"iv": "2c59487653a441b3fcf7624748d0f3bc", "encrypted_flag": "17b35f7948039116a933a17077802424d29138e30a4ae074a076fe84dab7469e"}from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
import hashlib
def is_pkcs7_padded(message):
padding = message[-message[-1]:]
return all(padding[i] == len(padding) for i in range(0, len(padding)))
def decrypt_flag(shared_secret: int, iv: str, ciphertext: str):
# Derive AES key from shared secret
sha1 = hashlib.sha1()
sha1.update(str(shared_secret).encode('ascii'))
key = sha1.digest()[:16]
# Decrypt flag
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
iv = bytes.fromhex(iv)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
if is_pkcs7_padded(plaintext):
return unpad(plaintext, 16).decode('ascii')
else:
return plaintext.decode('ascii')
shared_secret = 0
iv = 'ec5f47b6f57ca9473ad45a8712b26fdb'
ciphertext = '9a2a60454a75ce5dfa19b117569be48890e76731fa07141756bc23dfebafa07e'
print(decrypt_flag(shared_secret, iv, ciphertext))方法二:pwntools
将 p 的值修改为 1,这样 DH 加密过程中的
import json
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from pwn import *
def is_pkcs7_padded(message):
padding = message[-message[-1]:]
return all(padding[i] == len(padding) for i in range(0, len(padding)))
def decrypt_flag(shared_secret: int, iv: str, ciphertext: str):
# Derive AES key from shared secret
sha1 = hashlib.sha1()
sha1.update(str(shared_secret).encode('ascii'))
key = sha1.digest()[:16]
# Decrypt flag
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
iv = bytes.fromhex(iv)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
if is_pkcs7_padded(plaintext):
return unpad(plaintext, 16).decode('ascii')
else:
return plaintext.decode('ascii')
def main():
r = remote("socket.cryptohack.org", 13371) # 连接远程服务器
r.recvuntil(b"Intercepted from Alice: ")
intercepted_from_Alice = json.loads(r.recvline())
print(intercepted_from_Alice)
intercepted_from_Alice['p'] = "1"
r.recvuntil(b'Send to Bob: ')
r.sendline(json.dumps(intercepted_from_Alice).encode('utf8'))
# 接收来自 Bob 的参数:
r.recvuntil(b'Intercepted from Bob: ')
r.sendline(r.recvline())
r.recvuntil(b'Intercepted from Alice: ')
alice_cipher = json.loads(r.recvline())
print(alice_cipher)
shared_secret = 0
iv = alice_cipher["iv"]
cipher = alice_cipher["encrypted_flag"]
flag = decrypt_flag(shared_secret, iv, cipher)
log.info(flag)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()Export-grade
选择DH64,降低加密级别,用sympy解离散对数就能得到私钥 Key了
获取私钥 key值
from sympy import discrete_log
p=0xde26ab651b92a129
g=0x2
A=0x6ad5a3a6ae86c5b
B = 0x56860ea0eae02d15
a = discrete_log(p,A,g)
k = pow(B,a,p)
# print(a)
print(k)
#key = 14860681225588294227pwntools交互脚本
import json
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad
from pwn import *
from sympy import discrete_log
def is_pkcs7_padded(message):
padding = message[-message[-1]:]
return all(padding[i] == len(padding) for i in range(0, len(padding)))
def decrypt_flag(shared_secret: int, iv: str, ciphertext: str):
# Derive AES key from shared secret
sha1 = hashlib.sha1()
sha1.update(str(shared_secret).encode('ascii'))
key = sha1.digest()[:16]
# Decrypt flag
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
iv = bytes.fromhex(iv)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
if is_pkcs7_padded(plaintext):
return unpad(plaintext, 16).decode('ascii')
else:
return plaintext.decode('ascii')
def main():
r = remote("socket.cryptohack.org", 13379) # 连接远程服务器
r.recvuntil(b"Intercepted from Alice: ")
r.recvline()
r.recvuntil(b"Send to Bob: ")
r.sendline(b'{"supported": ["DH64"]}')
r.recvuntil(b'Intercepted from Bob: ')
x = r.recvline()
r.recvuntil(b'Send to Alice: ')
r.sendline(x)
r.recvuntil(b'Intercepted from Alice: ')
intercepted_from_Alice1 = json.loads(r.recvline())
r.recvuntil(b'Intercepted from Bob: ')
intercepted_from_Bob = json.loads(r.recvline())
r.recvuntil(b'Intercepted from Alice: ')
intercepted_from_Alice2 = json.loads(r.recvline())
print("intercepted_from_Alice1 = ", intercepted_from_Alice1)
print("intercepted_from_Bob = ", intercepted_from_Bob)
print("intercepted_from_Alice2 = ", intercepted_from_Alice2)
# 计算Alice的私钥a,解离散对数
p, g, A = int(intercepted_from_Alice1['p'], 16), int(intercepted_from_Alice1['g'], 16), int(
intercepted_from_Alice1['A'], 16)
a = discrete_log(p, A, g)
B = int(intercepted_from_Bob['B'], 16)
k = pow(B, a, p) # 计算共享密钥k
iv, ciphertext = intercepted_from_Alice2['iv'], intercepted_from_Alice2['encrypted_flag']
flag = decrypt_flag(k, iv, ciphertext)
print(flag)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()椭圆曲线
在公钥加密中使用椭圆曲线于 1985 年首次提出。在抵御了数十年的攻击之后,它们从 2005 年左右开始得到广泛使用,与以前的公钥密码系统(例如 RSA)相比,具有多种优势。
较小的 EC 密钥可提供更大的强度,256 位 EC 密钥具有与 3072 位 RSA 密钥相同的安全级别。此外,使用这些密钥的多项操作(包括签名)在时间和内存方面都可以更加高效。最后,由于 ECC 比 RSA 更复杂,因此它具有鼓励开发人员使用可信库而不是自己开发库的可喜效果。
本课程旨在让您直观地了解 ECC 背后的陷门功能;深入了解其背后的数学结构;您是否破坏了 ECDSA 等流行方案。
Background Reading(背景知识)
椭圆曲线密码学 (ECC) 是一种非对称密码协议,与 RSA 和 Diffie-Hellman (DH) 一样,它依赖于陷门函数(trapdoor function)。回顾一下:陷门函数允许客户端通过执行数学运算来保密数据,这在计算上很容易做到,但目前认为撤消的代价非常高。对于 RSA,陷门函数依赖于分解大数的难度。对于 Diffie-Hellman,陷门依赖于离散对数问题的难度。对于 RSA 和 DH,我们都熟悉贯穿协议脉络的操作。
乘法和求数的幂是我们在学校被教导要做的事情。ECC脱颖而出,因为ECC中的组操作除非你自己去找,否则不会出现在你的生活中。
提示
推荐学习笔记:[ Ben Lynn 的椭圆曲线笔记 ](https://web.archive.org/web/20220412170936/https://crypto.stanford.edu/pbc/notes/elliptic/)
从椭圆曲线的含义开始思考 ECC。研究 Weierstrass 方程,其形式为:
椭圆曲线有一个惊人的特性:我们可以定义一个我们称之为**“点加法”的运算符**。该运算符在某些曲线上取两个点并在曲线上产生第三个点。取椭圆曲线上的点集,点加法定义了阿贝尔群运算。
提示
我们可以把一个点的标量乘法理解为同一个点的重复点加法。 Q = 2P = P + P . 事实证明,标量乘法是一个陷门函数!ECC 依赖于找到 n 的难度,例如 Q = nP ,给定 Q、P
那么我们怎么理解点加法呢?
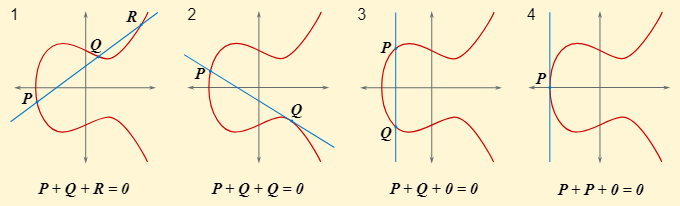
在几何上,我们可以这样理解点加法 P+Q 。取一条椭圆曲线并用 x,y 坐标标记沿曲线的 P , Q 两个点。画一条通过两点的直线。现在继续这条线,直到它第三次与你的曲线相交。标记这个新交叉点 R 。最后,取 R 并沿 y 方向反射它以产生 R' = R(x,-y) 。点加的结果是 P + Q = R'
如果我们想将两个相同的点加在一起: P + P 怎么办?我们不能通过一个点来画出一条唯一的线,但我们可以通过计算曲线在点 P 处的切线来选择一条唯一的线。继续这条线,直到它与曲线相交于点 R 。像之前一样反射该点: P + P = R' = R(x,-y) 。
如果没有第三个交点会怎样?有时你会选择两个点 P, Q,使得直线不会再次接触曲线。在这种情况下,我们说这条线与点 (O)相交,该点是位于无穷远处每条垂直线末端的单个点。因此,椭圆曲线的加点是在二维空间中定义的,附加点位于无穷远处。
下面包括一个图表,作为这些不同情况的视觉辅助:
点
相关信息
这让我们想到了定义椭圆曲线的点。
**定义:**椭圆曲线 E 是 Weierstrass (魏尔斯特拉斯方程) 的解集,
连同无穷大
形式上,设 E 为椭圆曲线,点加法具有以下性质:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
在 ECC 中,我们研究有限域
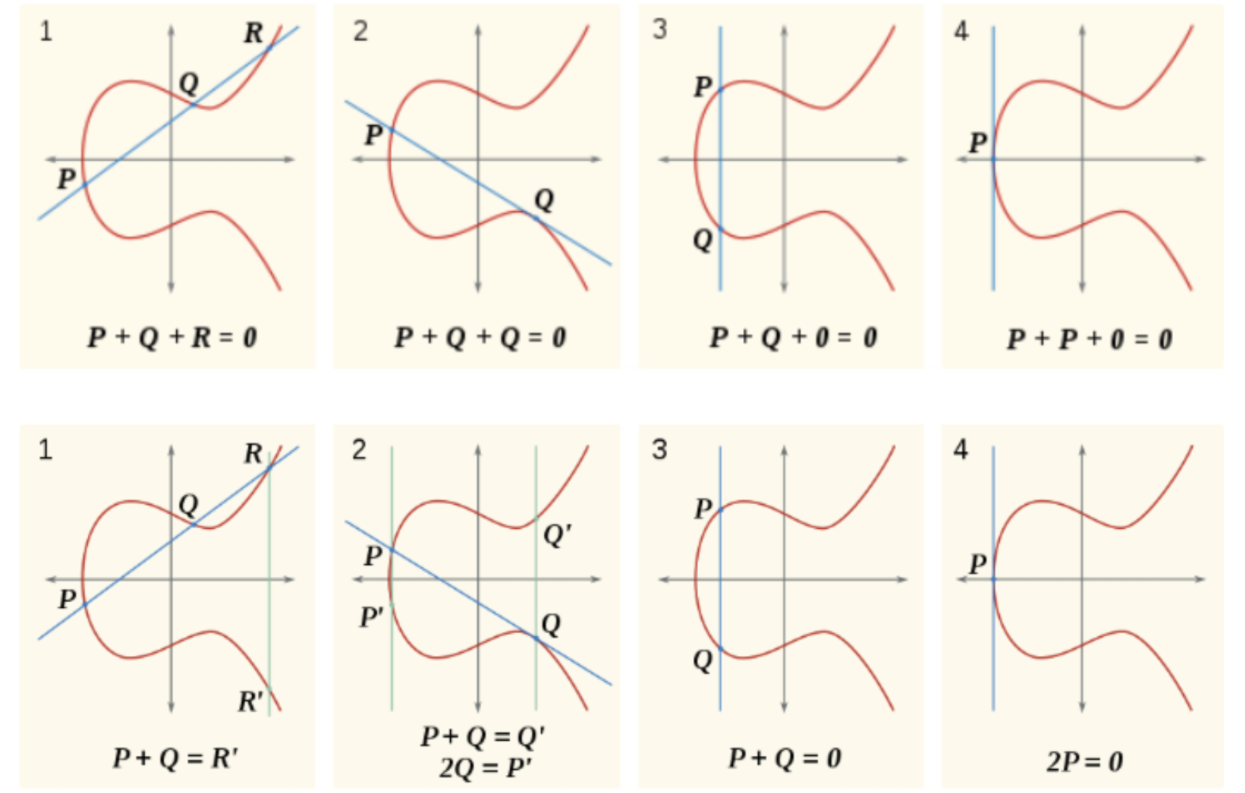
Point Negation(对称点)
为了应用椭圆曲线到密码系统中,我们研究了在有限域中具体坐标的椭圆曲线。
我们考虑形式为 :
因此,我们不再认为椭圆曲线是一个几何对象,而是由一组点
例题:
使用上面的曲线和点
解析:
根据条件可知有限域为:
由
Point Addition(点加)
在学习椭圆曲线加密时,我们需要将点加在一起,在几何上我们实现的方法是:用直线连接曲线上的两点 P、Q,并继续延伸与曲线交于新的点 R,然后沿y轴反射来找到关于x轴对称的点 R' ,即 P + Q = R' 。如下图所示。
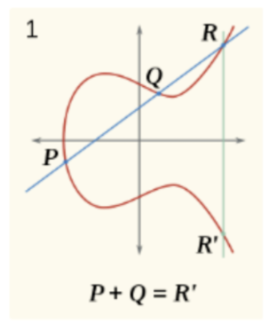
现在我们需要用算法来实现这一步骤,算法摘自《An Introduction to Mathematical Cryptography》这本书
以下算法将计算椭圆曲线上两个点的相加:

你可以通过断言测试你的算法:
X = (5274, 2841) and Y = (8669, 740) ==>
X + Y = (1024, 4440) ,X + X = (7284, 2107) .
python算法实现:
from gmpy2 import invert
O = (0, 0)
def point_add(p, q):
if p == O:
return q
elif q == O:
return p
else:
x1, y1 = p
x2, y2 = q
if x1 == x2 and y1 == -y2:
return O
if p != q:
lmd = (y2 - y1) * invert(x2 - x1, Fp)
if p == q:
lmd = (3 * x1**2 + a) * invert(2 * y1, Fp)
x3 = (lmd**2 - x1 - x2) % Fp
y3 = (lmd * (x1 - x3) - y1) % Fp
return x3, y3
# E: Y^2 = X^3 + 497X + 1768, p: 9739
a = 497
b = 1768
Fp = 9739
# 算法test代码
X = (5274, 2841)
Y = (8669, 740)
assert point_add(X, Y) == (1024, 4440)
assert point_add(X, X) == (7284, 2107)
print("ok")**sage实现:**先生成一个有限域
from sage.all import EllipticCurve
a = 497
b = 1768
Fp = 9739
E = EllipticCurve(Zmod(Fp),[a,b])
# Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 = x^3 + 497*x + 1768 over Ring of integers modulo 9739
X = E([5274, 2841])
Y = E([8669, 740])
assert (X + Y).xy() == (1024, 4440)
assert (X + X).xy() == (7284, 2107)
print("ok")EllipticCurve(R,[a,b])函数用于构建椭圆曲线对象。其参数包括:
R:构建域定义域,表示椭圆曲线上的坐标的取值范围
a, b:椭圆曲线方程的系数
.xy()函数返回点的坐标元组。
例题:
使用上面的曲线和介绍的点加的算法,给定点
解析:
利用上面实现的算法计算即可:
P = (493, 5564)
Q = (1539, 4742)
R = (4403, 5202)
S = point_add(point_add(P, P), point_add(Q, R))
print(S)(mpz(4215), mpz(2162))
Scalar Multiplication(标量乘法)
在椭圆曲线的加密和数字签名算法中,Scalar Multiplication 是指将一个标量(scalar)和一个点(point)相乘的操作,其结果是在椭圆曲线上另一个点。
具体来说,如果有一个椭圆曲线上的点
数学表示:
例如,如果
两点的标量乘法由重复加法定义:
用《An Introduction to Mathematical Cryptography》这本书中介绍的算法有效地计算椭圆曲线上点的标量乘法

使用的椭圆曲线:
给定点
python算法实现:
def Point_add(v1, v2):
if v1 == O: # (a) If P = O, then P + Q = Q.
return v2
elif v2 == O: # (b) Otherwise, if Q = O, then P + Q = P.
return v1
else: # (c) Otherwise, write P = (x1, y1) and Q = (x2, y2).
x1, y1 = v1
x2, y2 = v2
if (x1 == x2) and (y1 == -y2): # (d) If x1 = x2 and y1 = −y2, then P + Q = O.
return O
else: # (e) Otherwise:
if v1 != v2: # (e1) if P ≠ Q: λ = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
l = (y2 - y1) * pow(x2 - x1, -1, p)
else: # (e2) if P = Q: λ = (3*x1^2 + a) / 2y1
l = ((3 * pow(x1, 2) + a) * pow(2 * y1, -1, p))
x3 = (l ** 2 - x1 - x2) % p # (f) x3 = λ2 − x1 − x2,
y3 = (l * (x1 - x3) - y1) % p # (f) y3 = λ(x1 −x3) − y1
return (x3, y3)
def Scalar_Multiplication(n, Q, R):
while n > 0: # 2. Loop while n > 0.
if n % 2 == 1: # 3. If n ≡ 1 mod 2, set R = R + Q.
R = Point_add(R, Q)
Q = Point_add(Q, Q) # 4. Set Q = 2 Q and n = ⌊n/2⌋.
n = n // 2
return R
a = 497
b = 1768
p = 9739
P = (2339, 2213)
O = (0, 0)
Q = P # 1. Set Q = P and R = O.
R = O
n = 7863
Qn = Scalar_Multiplication(n, P, R) # n * P
print(Qn) # (9467, 2742)sagemath写法:
sage: from sage.all import EllipticCurve
sage: a = 497
sage: b = 1768
sage: p = 9739
sage: E = EllipticCurve(Zmod(p),[a,b])
sage: E
Elliptic Curve defined by y^2 = x^3 + 497*x + 1768 over Ring of integers modulo 9739
sage: k = 7863
sage: P = E([2339,2213]) # 定义椭圆曲线上的点
sage: k*P # 直接数乘
(9467 : 2742 : 1)Curves and Logs(曲线和离散对数)
Curves(曲线):椭圆曲线是一种在平面上定义的曲线,它的方程可以写成
**Logs(对数):**在椭圆曲线加密中,离散对数问题是指找到一个整数
Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem(ECDLP :椭圆曲线离散对数问题)是找到一个整数 n 的问题,使得
就像我们遇到的离散对数问题一样,
注
在椭圆曲线密码学中,重要的是 G 的阶是素数。构建安全曲线很复杂,建议使用预构造曲线,其中向客户提供曲线、素数和要使用的生成器。
椭圆曲线上的共享密钥
Alice 和 Bob 同意了一个曲线
Alice 生成一个秘密随机整数
Bob 生成一个秘密随机整数
Alice 向 Bob 发送了
然后 Alice 计算
由于标量乘法的结合性,
Alice 和 Bob 可以使用
例题:
使用下面的曲线,素数和生成器
在 Alice 向你发送
通过计算 x 坐标的 SHA1 哈希值来生成密钥(取坐标的十进制表示形式并将其转换为字符串)。该标志是您找到的十六进制摘要。
python实现:
import hashlib
def Point_add(v1, v2):
if v1 == oo: # (a) If P = O, then P + Q = Q.
return v2
elif v2 == oo: # (b) Otherwise, if Q = O, then P + Q = P.
return v1
else: # (c) Otherwise, write P = (x1, y1) and Q = (x2, y2).
x1, y1 = v1
x2, y2 = v2
if (x1 == x2) and (y1 == -y2): # (d) If x1 = x2 and y1 = −y2, then P + Q = O.
return oo
else: # (e) Otherwise:
if v1 != v2: # (e1) if P ≠ Q: λ = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
l = (y2 - y1) * pow(x2 - x1, -1, p)
else: # (e2) if P = Q: λ = (3*x1^2 + a) / 2y1
l = ((3 * pow(x1, 2) + a) * pow(2 * y1, -1, p))
x3 = (l ** 2 - x1 - x2) % p # (f) x3 = λ2 − x1 − x2,
y3 = (l * (x1 - x3) - y1) % p # (f) y3 = λ(x1 −x3) − y1
return (x3, y3)
def Scalar_Multiplication(n, Q, R):
while n > 0: # 2. Loop while n > 0.
if n % 2 == 1: # 3. If n ≡ 1 mod 2, set R = R + Q.
R = Point_add(R, Q)
Q = Point_add(Q, Q) # 4. Set Q = 2 Q and n = ⌊n/2⌋.
n = n // 2
return R
a = 497
b = 1768
p = 9739
Qa = (815,3190)
O = oo
Q = Qa # 1. Set Q = P and R = O.
R = O
Nb = 1829
Qb = Scalar_Multiplication(Nb,Qa,R) # n * P
print(Qb) # (7929, 707)
print(hashlib.sha1(str(Qb[0]).encode("utf-8")).hexdigest())sagemath实现:
sage: from sage.all import EllipticCurve
....: a = 497
....: b = 1768
....: p = Zmod(9739)
....: E = EllipticCurve(p,[a,b])
....: G = E([1804,5368])
....: QA = E([815,3190])
....: kB = 1829
....: S = kB*QA
....: S
(7929 : 707 : 1)
sage: from hashlib import *
sage: "crypto{" + sha1(str(S[0]).encode("utf8")).hexdigest() + "}"
'crypto{80e5212754a824d3a4aed185ace4f9cac0f908bf}'Efficient Exchange(高效交换)
下面这个挑战,我们使用一个素数
使用下面的曲线,素数和生成器:
在 Alice 向你发送
{'iv': 'cd9da9f1c60925922377ea952afc212c', 'encrypted_flag': 'febcbe3a3414a730b125931dccf912d2239f3e969c4334d95ed0ec86f6449ad8'}
题目给了我们
sagemath脚本计算共享密钥
from Crypto.Util.number import inverse, long_to_bytes
from Crypto.Hash import SHA1
from gmpy2 import iroot
from sage.all import EllipticCurve
Qx = 4726
x = Qx
p = 9739
a = pow(x, 3, p) + 497 * x + 1768
# 判断 a 是否为模p的二次剩余
if pow(a, (p - 1) // 2, p) == 1 and p % 4 == 3:
y = pow(a, (p + 1) // 4, p)
print("Qy =",y)
a = 497
b = 1768
p = Zmod(9739)
E = EllipticCurve(p,[a,b])
Q = E([x,y])
k_B = 6534
S = k_B*Q
print("共享密钥 S =",S)
# Qy = 6287
# 共享密钥 S = (1791 : 2181 : 1)然后采用共享密钥
Montgomery's Ladder(蒙哥马利阶梯)
需要保证椭圆曲线上的点的标量乘法以恒定时间运行,关键的一部分基于蒙哥马利阶梯
side channel analysis(旁道攻击分析)
Timing attacks against ECDSA signing can leak information about the nonce
(针对ECDSA签名的时序攻击可以泄露当前相关的信息)
LadderLeak:一类新的侧信道漏洞,实现用于 ECDSA 标量乘法的蒙哥马利阶梯,该漏洞尤其出现在 OpenSSL 的几个最新版本中。使用傅里叶分析方法的许多理论改进来解决 HNP 问题(这种方法最初由 Bleichenbacher 提出),这让我们实际上打破了 LadderLeak 的易损性。
Montgomery curves(蒙哥马利曲线):
Addition formula for Montgomery Curve (Affine) :蒙哥马利曲线(仿射)加法公式
Input: P, Q in E(Fp) with P != Q
Output: R = (P + Q) in E(Fp)
Doubling formula for Montgomery Curve (Affine):蒙哥马利曲线(仿射)的加倍公式
Input: P in E(Fp)
Output: R = [2]P in E(Fp)
题目:
使用上的曲线和基点
G.x = 9, 通过上的算法实现找到点的 坐标(10进制表示)。
解题:求 G的坐标
1,python实现
from sympy import *
# 计算 y^2 = x^3 + 486662x^2 + x
x = 9
p = 2 ** 255 - 19
assert p % 8 == 5
A = 486662
a = (pow(x, 3, p) + A * pow(x, 2, p) + x)
# 判断 a 是否为模 p 的二次剩余
assert pow(a, (p - 1) // 2, p) == 1
# 二次剩余的解
y = sqrt_mod(a, p, True)
print("y =", y)
print("G({},{})".format(x, y))2,sagemath实现
from sage.all import GF,EllipticCurve
p = (2**255) - 19
# y^2 + a_1 xy + a_3 y = x^3 + a_2 x^2 + a_4 x + a_6
E = EllipticCurve(GF(p), [0,486662,0,1,0])
G = E.lift_x(9)
k = 0x1337c0decafe
print("G =",G)
Q = k*G
print("Q的x坐标:",Q.xy()[0])
# G = (9 : 43114425171068552920764898935933967039370386198203806730763910166200978582548 : 1)
# Q的x坐标: 49231350462786016064336756977412654793383964726771892982507420921563002378152使用上面提到的蒙哥马利曲线 double_and_add 算法
from Crypto.Util.number import *
def Point_add(v1, v2):
if v1 == oo:
return v2
elif v2 == oo:
return v1
else:
x1, y1 = v1
x2, y2 = v2
if (x1 == x2) and (y1 == -y2):
return oo
else:
if v1 != v2: #if P != Q
l = (y2 - y1) * inverse(x2 - x1,p) # α = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1 )
x3 = (l ** 2 - A - x1 - x2) % p # x3 = B*α2 - A - x1 - x2
y3 = (l * (x1 - x3) - y1) % p # y3 = α(x1 - x3) - y1
return (x3,y3)
else: # if P == Q
l = ((3 * pow(x1, 2) + 2*A*x1 + 1) * inverse(2*y1,p)) # α = (3*x1^2 + 2*A*x1 + 1) / (2*B*y1)
x3 = (l ** 2 - A -2*x1) % p # x3 = B*α^2 - A - 2*x1
y3 = (l*(x1-x3) - y1) % p # y3 = α(x1 - x3) - y1
return (x3, y3)
#Montgomery’s binary algorithm in the group E(Fp)
def bin_montgomery(k,R0,R1):
nbit = bin(k)[3:] # 从高位计算到地位一共计算了 l - 1 次 ( l 为 k的长度),二进制序列第1个1不需要考虑
for i in range(len(nbit)):
if nbit[i] == "0":
R1 = Point_add(R0, R1)
R0 = Point_add(R0, R0)
else:
R0 = Point_add(R0, R1)
R1 = Point_add(R1, R1)
return R0
A = 486662
p = 2**255 - 19
P = (9,43114425171068552920764898935933967039370386198203806730763910166200978582548)
R0 = P
R1 = Point_add(P,P)
k = 0x1337c0decafe
Q = bin_montgomery(k,R0,R1) # Q = [k]*P
print(Q)crypto{49231350462786016064336756977412654793383964726771892982507420921563002378152}
Smooth Criminal(犯罪高手)
根据题目代码可知,我们发送给 Bob 的公钥信息 A 、椭圆曲线的基点 G,利用这个条件我们需要解决 DLP 离散对数问题,根据公式 discrete_log() 函数计算出我们的私钥
sage实现代码:
from sage.all import EllipticCurve,discrete_log
p = 310717010502520989590157367261876774703
a = 2
b = 3
E = EllipticCurve(GF(p),[a,b])
g_x = 179210853392303317793440285562762725654
g_y = 105268671499942631758568591033409611165
G = E([g_x,g_y]) # 基点
# 我的公钥信息
A_x=280810182131414898730378982766101210916
A_y=291506490768054478159835604632710368904
A = E([A_x,A_y])
k_a = discrete_log(A,G,operation="+")
print("k_a =",k_a)
# k_a = 47836431801801373761601790722388100620
# Bob的公钥
b_x = 272640099140026426377756188075937988094
b_y = 51062462309521034358726608268084433317
B = E([b_x, b_y])
# 计算共享公钥
S = B*k_a
x = S.xy()[0]
print("共享密钥 S 的 x 坐标为:",x)
# k_a = 47836431801801373761601790722388100620
# 共享密钥 S 的 x 坐标为: 171172176587165701252669133307091694084解flag
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import hashlib
def decrypt_flag(shared_secret: int, iv: str, encrypted: str):
sha1 = hashlib.sha1()
sha1.update(str(shared_secret).encode('ascii'))
key = sha1.digest()[:16]
# decrypt flag
iv = bytes.fromhex(iv)
decrypted = bytes.fromhex(encrypted)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(decrypted)
return plaintext, sha1
# decrypt flag
iv = '07e2628b590095a5e332d397b8a59aa7'
encrypted_flag = '8220b7c47b36777a737f5ef9caa2814cf20c1c1ef496ec21a9b4833da24a008d0870d3ac3a6ad80065c138a2ed6136af'
shared_secret = 171172176587165701252669133307091694084
print(decrypt_flag(shared_secret, iv, encrypted_flag))